Managing Virtual Hosts

Managing Virtual Hosts
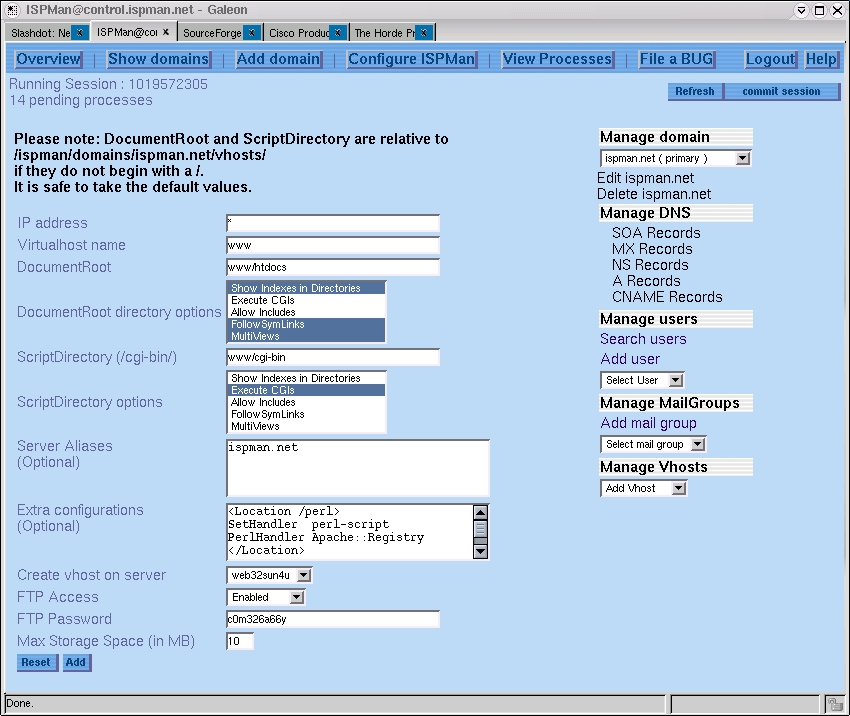
This screen allows the help-desk user to assign different properties and defaults to the newly created virtual host
- IP Address - This can be usually set to *. In most hosting environment it works fine.
Or it can be set to an IP Address. Previous versions of Apache required an IP address to be present when creating Name based Virtual hosts.
Now it is no longer a requirement.
- VirtualHost name - This is the short name of the virtual host.
The complete name is generated joining this name with the domain name using a "." character.
- Document root - This is the relative name to the homedirectory of the domain / vhosts.
So in this example the path would be translated to /ispman/domains/ispman.net/vhosts/www/htdocs
- Document root options - Options that can be set to this directory.
Example: Show directory listing, allow execution of CGI, etc.
- CGI script root - This is the relative name to the homedirectory of the domain / vhosts.
So in this example the path would be translated to /ispman/domains/ispman.net/vhosts/www/cgi-bin
- CGI script options - same as Document root options.
- ServerAliases - A server can be aliased to many different named.
Most commonly www.domain.name is aliased to domain.name.
- Extra configuration - If there is some extra configuration required for this vhost, the admin can enter it here.
- webserver for this host - In web server farms, you may want to distribute your virtual hosts to different servers.
-
Each Virtual host is a special kind of user.
This user gets
a username ("name of the virtual host") example "www.ispman.net",
a password
a disk quota
This user can log in via FTP if FTP status is enabled.
This is useful if there are different people taking care of different sites.
Example: you may give password for newdesign.ispman.net to your gfx agency but not for your complete domain or for intranet.ispman.net
